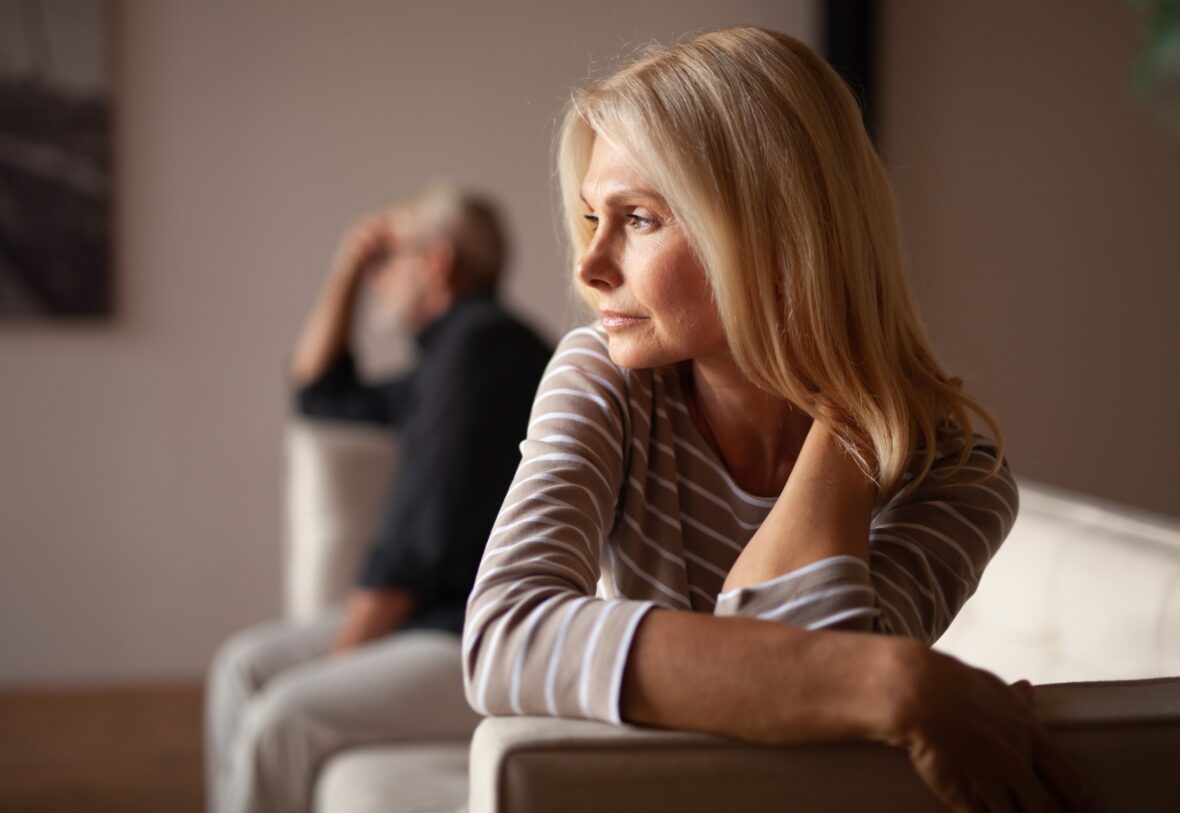
Depression (major depressive disorder) is a common and serious medical illness that affects an estimated 16 million American adults and children. It causes severe symptoms that affect how the person feels, thinks, and handles daily activities, such as sleeping, eating, or working. Depression is highly treatable with reports of 80% to 90% of people responding well to treatment.

Overview:
Depression (major depressive disorder) is a common and serious medical illness that affects an estimated 16 million American adults and children. It causes severe symptoms that affect how the person feels, thinks, and handles daily activities, such as sleeping, eating, or working. Depression is highly treatable with reports of 80% to 90% of people responding well to treatment.
Types:
Some forms of depression are slightly different, or they may develop under unique circumstances, such as:
Persistent depressive disorder:
Persistent depressive disorder, also called dysthymia, is a continuous, long-term (chronic) form of depression lasting for at least two years. Someone who is diagnosed with persistent depressive disorder may lose interest in normal daily activities, feel hopeless, lack productivity, and have low self-esteem.
Postpartum depression:
Postpartum depression is a lot more powerful and lasts longer than the “baby blues” (when new mothers feel a little sad, worried, or fatigued for a week or two following childbirth). Women with postpartum depression experience major depression following delivery. It can cause severe mood swings, exhaustion, and a sense of hopelessness.
Psychotic depression:
Psychotic depression occurs when a severe depressive illness includes some form of psychosis. The psychosis can include hallucinations or delusions. People with psychotic depression may get angry for no apparent reason or spend a lot of time by themselves.
Seasonal affective disorder:
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that’s related to changes in seasons. This depression generally starts during the winter months, when there is less natural sunlight, and lifts during spring and summer. Those who have seasonal affective disorder may experience symptoms such as oversleeping, appetite changes, weight gain, and low energy.
Symptoms:
Symptoms can vary from mild to severe and can include:
- Feeling sad or having a depressed mood
- Trouble sleeping or sleeping too much
- Loss of energy or increased fatigue
- Feeling worthless or guilt
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Changes in appetite (weight loss or gain)
- Thoughts of death or suicide
Causes:
It is often said that depression results from a chemical imbalance, but research suggests that there are many possible causes of depression, including faulty mood regulation by the brain, genetic vulnerability, stressful life events, medications, and medical problems.
Treatment:
At Mile High Psychiatry, we find a combination of therapy and medication to be a suitable treatment for depression in children and adults. Various forms of therapy can include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), and problem-solving therapy. Medication needs will vary from patient to patient, depending on the severity of the disorder.
Do you have questions regarding depression for yourself or your child? Request an appointment with Mile High Psychiatry to learn more.
Contact
Mile High Psychiatry
Learn more about our services and schedule your appointment today by calling:
CALL NOW: (855) 973-0166